You may be wondering if you should choose hemp protein vs pea protein when selecting a plant based protein powder.
It can be daunting to select a protein powder when you are presented with what seems like an endless number of options to choose from.
There are animal-based options such as whey and casein, as well as plant-based options such as hemp, pea, chia, rice or even blends of multiple types of these proteins.
Plant-based proteins have been increasing in popularity as people are becoming more conscious about their environmental impact and are choosing vegan or vegetarian lifestyles.
In this article, we will focus on hemp protein and pea protein. If you are interested in learning more about these two plant-based options and how to choose the best option, keep reading!
*Please note that this post contains clearly identified affiliate links. If you click on these links and choose to make a purchase, I may receive a commission (at no cost to you). As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Top Takeaways
- Plant-Based Protein Options: When considering plant-based protein powders, hemp and pea protein are two popular choices among various alternatives.
- Protein Quality Evaluation: The concept of “complete” proteins based on all nine essential amino acids is outdated. Protein quality is now assessed using the Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Scores (PDCAAS), which measure bioavailability and digestibility.
- Hemp Protein: Derived from hemp seeds, hemp protein is a source of all essential amino acids but lacks sufficient lysine, making it incomplete. It has a PDCAAS score of around 0.5 and offers additional benefits like fiber, healthy fats, and various minerals.
- Pea Protein: Pea protein, sourced from yellow split peas, is highly bioavailable, contains all essential amino acids, and boasts a high PDCAAS score of 0.82. It excels in protein content and muscle-building potential, making it suitable for those seeking a protein-focused option.
Are Plant-Based Proteins Good Protein Sources?
We eat protein for a variety of reasons. To help increase our muscle mass and strength, it can reduce appetite and hunger levels and it’s even good for our bones!
When choosing protein sources, it was once believed that some protein sources were better than others based on their amino acid composition. For example, if they contained the nine essential amino acids, they were referred to as “complete” proteins.
These nine essential amino acids are important to eat because our bodies are unable to make them on their own. However, research has concluded that you do not need to eat all nine essential amino acids at the same time to reap their benefits, and thus labeling a protein source as “complete” is obsolete (1).
Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Scores
Instead, a great way to measure the quality of proteins is to use the Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Scores (PDCAAS). This scale ranges from 0-1, with a ranking of 1 being the highest bioavailability, and 0 being the lowest (2).
These scores help indicate the bioavailability and digestibility of a protein source. Bioavailability refers to how much of a nutrient is actually being absorbed by our bodies. If a nutrient found in a specific food source is said to be highly bioavailable, this means that we can easily absorb it from this food.
We will use the PDCAAS ranking to determine protein quality, instead of outdated research that labels proteins as complete or incomplete based on their nine essential amino acid composition. A high PDCAAS score indicates that the protein is highly bioavailable.
Not to mention, plant-based proteins are great for improving heart health as they are lower in cholesterol and saturated fats when compared to animal-based proteins.
What is Hemp Protein?
Hemp protein is made from hemp seeds, which are known as a superfood. They come from the Cannabis Sativa plant. In order to make the protein powder, the seeds are pressed to remove the oil, then ground into a powder.
As a side note, you cannot get high from hemp, even though it originates from the same plant as marijuana. Hemp does not contain enough THC, which is the chemical in marijuana that causes psychoactive effects (3).
Color and Taste
Hemp protein is brownish-green in color and has a nutty, earthy taste. It is stronger in flavor compared to other protein powders, however, if this is a concern for you, you can mask the flavor by incorporating the protein into a smoothie or even baked goods.
Protein Quality
Hemp protein contains all nine essential amino acids but is still considered to be an incomplete protein, as it does not quite contain enough of the amino acid called lysine.
Hemp protein has a PDCAAS score of approximately 0.5 (4).
Nutrition Profile
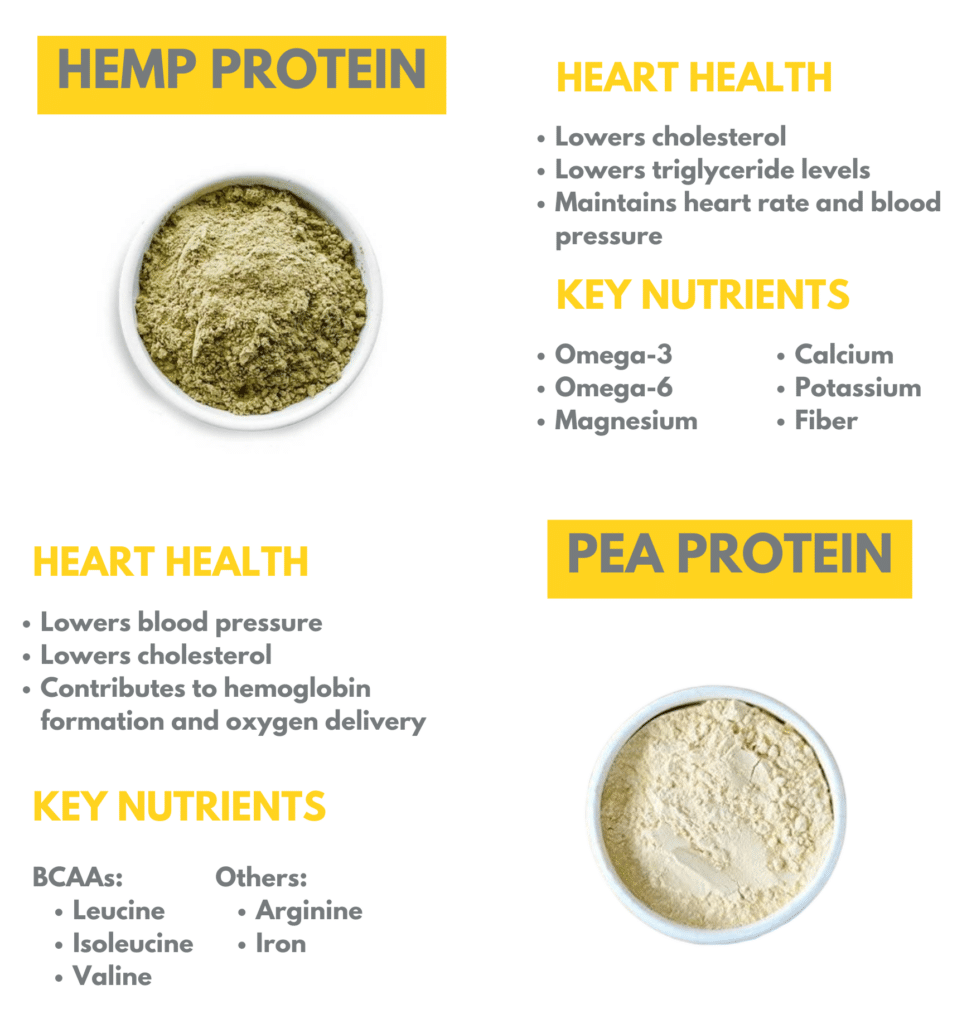
Hemp protein is rich in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, omega-6 fatty acids, magnesium, calcium, and potassium.

Nutrients
Fiber
Hemp protein is rich in both soluble and insoluble fiber. Both types of fiber aid in digestion, and soluble fiber in particular helps to lower cholesterol levels, increasing heart health (5).
Omega 3
Hemp protein is a good source of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are heart-healthy because they are excellent for lowering triglyceride levels in the blood and decreasing blood pressure. High levels of triglycerides can result in build-ups in the arteries which increase the risk of heart attack (6).
Minerals
Magnesium, calcium, and potassium are all important for maintaining heart rate and blood pressure.
They are involved in muscle contractions and therefore are needed to maintain a regular heart rate and blood vessel contraction and relaxation. For example, magnesium causes muscles to relax while calcium and potassium cause muscles to contract (7).
Brands Recommended by a Dietitian
When comparing brands, it is important to look at the ingredients used. When you look at the ingredient list, be sure to look for any additives or sweeteners.
Additionally, it is also important to compare the nutrition facts panel and the product’s nutrients per serving. Here are a few hemp protein brands that have been recommended by a dietitian.
Nutiva Hemp Protein Powder
The Nutiva Hemp Protein is an excellent option as it only contains one ingredient. They offer two types of hemp protein as well: peak protein or fiber plus. Fiber plus is a good option if you are looking for to add fiber to your eating pattern.
In a serving size of 4 tbsp (30 g) of peak protein:
- 15 g of protein
- 6 g of fiber and
- 3 g of fat
In a serving size of 4 tbsp (30 g) of fiber plus:
- 11 g of protein
- 11 g of fiber
- 2.5 g of fat
Bob’s Red Mill Hemp Protein Powder
The Bob’s Red Mill Hemp Protein is affordable and only contains one ingredient. An additional benefit is that it contains more iron and fiber compared to other brands.
In a serving size of ¼ cup (31 g):
- 14 g of protein
- 8 g of fiber
- 3 g of fat
Hemp Yeah! Max Protein Powder
This brand carries a few different options for hemp protein powders, but the max protein powder offers the most protein and is also unsweetened. Thus, it contains no added sugars.
If you are looking for a flavored powder, they also offer both chocolate and vanilla options that will contain some added sweetener.
In a serving size of 4 tbsp (32 g) of max protein:
- 20 g of protein
- 3 g of fiber
- 6 g of fat
What is Pea Protein?
Pea protein is made from yellow split peas. To make the protein powder, the outer shell is first removed, then the peas are ground into flour. To separate the protein from this flour mixture, wet filtration is used.
This results in a paste containing protein, vitamins, and minerals. Finally, this paste is dried into a powder, which is the final product we consume.
Pea proteins can come as either an isolate or concentrate. The main difference between these two is the amount of protein per serving. Isolates will contain more protein than concentrates as they are further refined.
Color and Taste
Pea protein powder is light yellow in color and has a slightly earthy flavor. In comparison to hemp protein, pea protein has a much milder taste.
Protein Quality
Pea protein contains all the essential amino acids, however, like hemp protein, is still considered to be incomplete because it is low in the amino acids methionine and cysteine.
The PDCAAS of pea protein is 0.82 (8), which is very high and similar in score to animal-based sources of protein, which are known as higher-quality proteins.
Nutrition Profile
Pea protein has a very high protein content. The powders are usually made up of around 90% protein, and therefore do not contain large amounts of micronutrients but they are a good source of iron.
Specifically, pea protein contains significant amounts of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which are involved in muscle protein synthesis. These include leucine, isoleucine and valine.
It also contains large amounts of the amino acid arginine.
Nutrients
Amino Acids
Through animal studies, it has been shown that pea protein helps to reduce cholesterol and lowers blood pressure, both of which are important for maintaining heart health (9).
The amino acid arginine is involved in increasing blood flow and, in turn, oxygen flow. Arginine is converted into nitric oxide in the body, which is known to help widen blood vessels (10). This can help with lowering blood pressure.
As previously mentioned, pea protein has a very high PDCAAS. It is more bioavailable than other plant-based protein powders and is most comparable to animal-based proteins. This means your body can absorb and use more of the protein found in the product.
The BCAAs, leucine, isoleucine, and valine in pea protein make it an excellent choice if you are looking to build muscle. They help with muscle growth and help eliminate some muscle soreness that results from training (11).
Iron
Pea protein is an excellent source of iron, which is needed to form hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the part of a red blood cell that carries oxygen (12).
Our blood delivers oxygen to muscles and organs throughout the entire body, including the heart. The heart is also responsible for pumping our blood. If the heart does not get enough oxygen, this will cause stress and increase the risk of a heart attack.
Low In Carbohydrates
Finally, pea protein is low in carbohydrates. This makes it a good option for those with diabetes who need to consume fewer carbohydrates to help maintain blood glucose levels.
Brands Recommended by a Dietitian
NOW Sports Organic Pea Protein
In a serving size of one scoop (33 g):
- 24 g of protein.
This unflavoured NOW Sports Organic Pea Protein is a good option because it only contains one ingredient, avoiding the use of additives and sweeteners.
Naked Nutrition Naked Pea Protein Powder
In a serving size of two scoops (30 g):
- 27 g of protein.
This option is great because it offers a high amount of protein and contains no additives or sweeteners.
Anthony’s Pea Protein
In a serving size of 1 tbsp (10 g):
- 8 g of protein.
This is another great option because, like the other two, it is unflavoured and contains no added sugars or sweeteners. It has a very high amount of protein as well, offering 8 g per serving.
Summary of Hemp vs Pea Protein
The table below provides a summary of the nutritional qualities of hemp protein and pea protein based on the recommended brands and serving sizes of 30 grams.
| Hemp Protein | Pea Protein | |
| Average protein per serving (g) | 16 g | 26 g |
| Average carbs per serving (g) | 8 g | 2 g |
| Average fat per serving (g) | 3 g | 2 g |
| Average fiber per serving (g) | 7 g | 0.3 g |
| Key Additional Nutrients | Omega-3, omega-6, magnesium, calcium, potassium | Iron |
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Pea Protein or Hemp Protein Better?
Hemp protein offers more fiber, healthy fats, and micronutrients than pea protein. While pea protein offers more bioavailable protein.
Can You Build Muscle with Pea Protein?
Yes, you can build muscle with pea protein. The BCAAs found in pea protein are important for building muscle mass and muscle recovery. So alongside resistance training, pea protein can be used to build muscle.
Can You Lower Blood Pressure with Pea Protein?
Yes, pea protein is high in the amino acid arginine which helps to lower blood pressure by widening blood vessels.
Are Pea and Hemp Protein Complete Proteins?
Both hemp and pea proteins are incomplete. They contain all nine essential amino acids, but not in sufficient amounts to be considered complete. Keep in mind that this is not a concern if you are consuming other protein sources throughout the day.
Is Hemp a High-Quality Protein?
Hemp protein is a high-quality protein because it contains all the essential amino acids, but the amino acids in hemp protein are not as bioavailable as other protein options like pea protein (according to the PDCAAS scale).
Is Pea a High-Quality Protein?
Pea protein is a high-quality protein because it contains all the essential amino acids, and it is also very bioavailable.
Final Thoughts
So would you choose hemp protein or pea protein? Tell me in the comments below!
Both hemp and pea proteins offer health benefits that contribute to heart health. Choosing which option is best for you will depend more specifically on your health goals.
If you are concerned mainly with having a high protein content or looking to build muscle, pea protein would be the better option for you, as it is mainly protein and has a high bioavailability. It is also a better option if you are looking for a protein powder with a milder taste.
However, if you are not as concerned with a high protein content but are looking to increase your intake of other nutrients such as fiber and healthy fats, in addition to protein, then hemp protein would be the better option for you.
This article was written by Siobhan Tyler, Nutrition Student, and Veronica Rouse, MAN, RD, CDE.