You’ve likely seen names like ‘Atlantic Salmon’ or ‘Pacific Salmon’ in the supermarket, but have you ever wondered what the main difference is between these two?
Worry not, as this article will cover everything you need to know about Pacific vs Atlantic salmon, their health benefits, and other common questions regarding salmon.
This article was written by Chantel Alejado, Toronto Metropolitan University Nutrition Student. Medically reviewed by Veronica Rouse, MAN, RD, CDE
Top Takeaways
- Health Benefits of Salmon: Salmon is rich in heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) and can lower the risk of heart disease and improve heart health. It is recommended to consume at least 2 servings of salmon per week.
- Differences Between Pacific and Atlantic Salmon:
- Atlantic salmon has North American, European, and Baltic varieties, while Pacific salmon includes pink, chum, sockeye, coho, and chinook.
- Atlantic salmon has a milder taste and firmer texture, while Pacific salmon has a richer flavor and softer texture.
- Atlantic salmon has higher omega-3 content, while Pacific salmon offers more vitamins and minerals.
- Health Benefits and Mercury Content: Both types of salmon offer health benefits, but they have low mercury levels, making them safe to consume. Salmon is recommended for heart health and provides omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and essential nutrients.
- Environmental Impact and Considerations: Both Atlantic and Pacific salmon have environmental concerns, with Atlantic salmon often farmed and associated with pesticide use, while Pacific salmon faces challenges related to overharvesting and climate change. The choice between the two may depend on individual preferences and environmental considerations.
Pin It For Later!
Salmon And Heart Disease
Why is salmon so healthy you ask? Well, a substantial amount of research links salmon’s heart-healthy benefits to its omega-3 fatty acid content. Omega 3 fatty acids are essential for many bodily functions such as brain development, and salmon are rich sources of EPA and DHA.
Indeed, having at least 500 mg/day of eicosapentaenoic acids (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), two types of Omega 3 fatty acids, is recommended. Eating at least 2 servings of salmon per week can help you achieve this recommendation (1).
A recent study showed that fish consumption can lower your risk of heart disease (2). Another showed that EPA and DHA is related to improving heart health by decreasing inflammation and improving blood flow (1).
Salmon is one of 39 foods that can lower blood pressure and one of 39 foods that can unclog arteries.
These fish sources of omega 3 fatty acids are better absorbed in our body than plant sources. Plant sources of omega 3 fatty acids include linseeds, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds.
Pacific vs Atlantic Salmon Differences
Atlantic Salmon vs Pacific Salmon Definitions
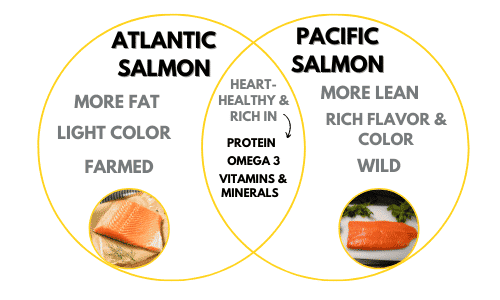
There are two different types of salmon – Atlantic and Pacific salmon.
Atlantic salmon has three major groups. The three types of Atlantic salmon are North American, European and Baltic which reside near the Atlantic Ocean (3).
Pacific salmon reside near the Pacific Ocean. They are categorized into seven specific groups or species of Pacific salmon. Five types of Pacific salmon live in North America; pink, chum, sockeye, coho, and chinook (also known as king salmon).
Appearance
Adult Atlantic salmon have thin long bodies, a silver coat with a white belly and dark-green spots across their body and head.
There are slight differences in appearance among the different Pacific salmon species. Still, they all have sliver bodies with some spots, except for chum and sockeye, which do not have spots.
Lifespan
Young salmon are called fry, which grow into parr in freshwater steams. They then develop into smolts in springtime, at which point they travel to the open ocean and remain there for 1 to 2 years to mature into adults. They return to freshwater to lay eggs and then the salmon swim back to the ocean afterward (4).
This is why both Atlantic and Pacific salmon are known to be “anadromous,” as they can live in both fresh and saltwater. They spawn in freshwater, mature in saltwater oceans, and return as adults to freshwater bodies.
Taste
When comparing Pacific vs Atlantic salmon, Atlantic salmon has a milder taste and Pacific salmon has a richer flavor.
P.S. If you aren’t sure about the taste of salmon and need a fantastic recipe, try this pesto butter salmon tonight!
Texture
Atlantic salmon has a firmer texture, while Pacific salmon has a softer texture.
Nutrition
Both Atlantic and Pacific salmon are great options for Omega 3! 200 g of an Atlantic salmon provides 8 g of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), which includes 2 g of both EPA and DHA, 40 g of protein, and a whopping 11.9 mcg of Vitamin D. This covers up to 80% of an adult’s recommended Vitamin D intake.
Pacific salmon are also great healthy options! 160 g of Pink salmon offers 33 g of protein, 4 g of PUFA (1 g of both EPA and DHA), and an even greater 17 mcg of Vitamin D!
Health Benefits
Both Atlantic and Pacific salmon are excellent sources of PUFA.
The difference between Atlantic and Pacific salmon is, Atlantic salmon has a higher Omega 3 content than Pacific. Omega 3s are not only great for reducing your risk of heart disease and maintaining heart health but also for improving brain health. DHA is vital for maintaining brain function and development (5).
Salmon is one of the top 39 foods that unclog arteries. In fact, the American Heart Association recommends regular intake of fish and suggests eating 2 to 3 servings of fish per week to lower your risk of heart disease (6).
Both types of salmon are also excellent sources of Vitamin D. Vitamin D is essential in maintaining strong, healthy bones and a strong heart. Studies have shown that Vitamin D plays a role in helping to manage blood pressure (7).
Mercury
Most fish have mercury, and the majority have levels safe to eat, including Atlantic and Pacific salmon. Both types of salmon have similar, low levels of mercury. Consuming high levels of mercury can still pose a significant health risk as it can impact brain development.
Children and pregnant and breastfeeding women are at risk for mercury exposure. However, salmon consumption is still perfectly safe and highly recommended due to its nutrition and health benefits (8).
Learn more about mercury at fish and what we can do about it here.
Environmental Impact
Atlantic salmon, often farmed and bred in controlled enclosures, presents various environmental issues. This includes excessive pesticide use that poses risks to human health and other marine life and fish waste leaking into nearby waters that could disturb local flora (9).
There are also many environmental issues surrounding Pacific salmon. Issues such as overharvesting of fish and climate change threaten their natural habitats (10).
Price
Prices depend on how you buy your salmon. Fillets will generally be more expensive than the whole salmon as they require more work to prepare.
Fresh Atlantic salmon fillet in 2022 costs around $30.84 per kg CAN, while a whole salmon costs $24.23 per kg CAN.
Pacific salmon is more commonly available in a can. A 142 g of canned Sockeye Salmon costs around $5.99 CAN per can.
Even though canned salmon is less expensive than fresh, fresh salmon is the more popular choice.
Color
Have you ever wondered when comparing Atlantic vs. Pacific salmon, which one is the deep red salmon you see in the grocery store?
It is usually Pacific salmon. Pacific salmon fillets tend to have a darker, rich, or deep red color as they are leaner. On the other hand, Atlantic salmon fillets have a lighter-red hue due to their higher-fat content.
Antibiotic Use
Atlantic salmon are more prone to antibiotics use than Pacific salmon as they are farmed, meaning their living conditions are heavily controlled. The use of antibiotics helps to prevent and treat disease among the fish.
But, antibiotic use in the farming industry is often uncontrolled. This can threaten our health and the environment due to antibiotic resistance, which is the concept of when we overuse antibiotics to the point where the bacteria targeted does not respond (11).
But, the good news is that countries like Canada have started to improve their salmon farming by lowering their antibiotic use in their farmed salmon (12).

Frequently Asked Questions
Scroll down for more salmon related questions answered!
Is Atlantic Or Pacific Salmon Better?
Atlantic salmon have a higher fat content than Pacific salmon, which means they have more Omega 3s and more saturated fats. Pacific salmon contains more vitamins and minerals such as calcium, Vitamin D, and iron.
But, both Atlantic and Pacific salmon are great seafood options that provide excellent heart-healthy benefits.
What Does Wild Salmon Mean?
Wild fish are caught from a natural environment; a lake, river, or ocean. Therefore wild salmon roam freely, often without any human interference, also known as the “free range” option. They are not fed a specific feed or antibiotics and are caught by fishers. Most Pacific salmon are wild.
Fishing for wild Atlantic salmon is prohibited in the United States, as wild stocks are declining and salmon populations are considered endangered. All Atlantic salmon in the grocery store is grown on fish farms or salmon farms.
What Does Farmed Salmon Mean?
Farmed salmon live in tanks or enclosures where their living conditions are controlled. This means they are fed specific fish feed to make them suitable for consumption.
The majority, if not all, of the Atlantic salmon is farmed. Because of the different conditions in which they live and the fish’s feeds, they vary from their Pacific counterparts nutritionally.
Which Is Healthier, Farmed Or Wild Salmon?
You may be wondering which is the healthiest salmon? Both farmed and wild salmon are healthy options and excellent choices for adding seafood into your diet and meeting the recommended guidelines. They are rich sources of omega 3 fatty acids, protein, Vitamin D and calcium!
Salmon may also contain contaminants such as PCB (stands for Polychlorinated Bisphosphate), but the levels present in fish is generally safe according to Health Canada standards. Farmed salmon may have higher levels as PCB is contained in fat, and farmed salmon have higher fat levels (13).
What Type Of Salmon Do They Use For Sushi?
Sushi is a popular Japanese dish that uses raw seafood. Atlantic farmed salmon is most commonly used for sushi as they are a low risk for parasites. Generally, salmon that has been previously frozen according to FDA guidelines is safe to use for home-making sushi.
Is Canned Salmon Healthy?
Canned fish is still a very healthy option and a cheaper one! Canned salmon is usually wild Pacific salmon, and thus you will usually see the term sockeye salmon vs. Atlantic salmon on the label.
Canned salmon provides you with essential nutrients like your Omega 3s, protein, and Vitamin D at a lower cost than your fresh salmon. Canned also extends the shelf life and is more readily available at grocery stores.
When choosing canned salmon, try to pick one that says “No sodium added” or “Low sodium” on the front of the label, as this is the best choice.
Canned goods may have added sodium to help preserve the foods and maintain food safety. Consuming too much sodium can increase blood pressure, and therefore may not be as heart-healthy.
Also, if you’re worried about mercury, canned salmon is usually younger and has less mercury!
Is Frozen Salmon Healthy?
Frozen fish is just as healthy as fresh salmon. Once you defrost frozen fish, it will still hold the same nutrients as its fresh counterpart.
Frozen holds the edge over fresh in that you can store it in your freezer for the long term if you decide to wait and use it in a future recipe.
Make sure to choose those that say “Frozen at sea” on the package, as this means that they were blast-frozen, which is a method of freezing that helps preserve the quality and nutrients of the fish.
Is Atlantic or Pacific Salmon More Commonly Consumed In The United States?
Atlantic salmon is more commonly consumed in the United States, and fresh salmon is more popular than canned salmon (14).
Final Thoughts
Salmon is a very healthy food and one to eat more of! Be sure to check out this post with over 30 heart-healthy salmon recipes.
Now you know the differences between Pacific vs Atlantic salmon, how they vary in their environmental living conditions and as a result, have slight nutritional differences. Atlantic salmon tend to have a light red color and have a high fat content. In contrast, Pacific salmon tend to have a richer, red hue and are leaner.
But whatever the type of salmon, they are both still excellent sources of omega 3s, protein, Vitamin D, and calcium.
If you are interested in learning other ways to eat well for your heart, download a FREE 7 day heart healthy meal plan when you subscribe to our monthly newsletter.


There is a local fish market nearby where we have recently bought what is labeled as ‘wild caught’ Atlantic Salmon. They claim it is from Newfoundland fishermen.
That’s wonderful Wayne! Enjoy it.
Useful information! Excellent overview. Just returned from Norway where we consumed copious quantities of Atlantic salmon. All delicious. Mild, nice texture, absolutely no “fishy” odor. Having some for dinner tonight Taak skal du ha! Thank you!
Vær så god Tony! I’m so happy you enjoyed the information. Happy eating 🙂
A round of applause for your blog post.Really thank you! Really Great.
I’m so glad you found this post informative.
V.