Picture this: you are in the kitchen, preparing a delicious meal for yourself or your loved ones. As you reach for a cooking fat, you’re faced with a dilemma— it is butter vs. olive oil.
Both have their own unique flavours and have been kitchen staples for centuries. But when it comes to heart health, which one takes the crown?
In this blog post, we are going to embark on a flavourful journey exploring the differences between butter and olive oil. We will dive into their types, unravel their nutritional secrets, and uncover the scientific evidence that can help us make an informed decision.
Top Takeaways
- Olive oil is a healthier choice compared to butter due to its lower saturated fat content, higher levels of heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, and various health benefits.
- Olive oil has anti-inflammatory properties, supports heart health, and may help reduce the risk of certain cancers.
- When cooking, olive oil has a higher smoke point, making it suitable for high-heat methods, while butter is better for lower-heat cooking. It is also a primary fat source in the Mediterranean diet.
- Olive oil can be a heart-healthy substitute for butter in many recipes, offering a unique flavor profile.
- Top Takeaways
- Watch The Summary Here
- Types Of Olive Oil
- Types Of Butter
- Nutritional Breakdown Of Olive Oil vs. Butter
- Health Benefits
- Which Is Better For Cholesterol And Heart Health?
- Cooking Properties
- Culinary Uses
- Sustainability
- Cost
- How They Are Used In The Mediterranean Diet
- How To Replace Butter With Olive Oil
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Recipes That Use Olive Oil For Heart Health
- Final Thoughts
Watch The Summary Here
Types Of Olive Oil
Olive oil, derived from the fruit of the olive tree, boasts a rich flavour and a host of health benefits. It comes in several varieties, including:
- Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO): Considered the highest quality and least processed form of olive oil, EVOO is obtained through cold pressing and does not undergo chemical refining. It retains a higher level of antioxidants and monounsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health (1).
- Virgin olive oil: Similar to EVOO, virgin olive oil is also obtained through the mechanical extraction of olives. It has a slightly higher acidity level and a milder flavour compared to EVOO but still offers heart-healthy monounsaturated fats (2).
- Refined olive oil: This type of olive oil undergoes further processing, such as refining and filtering, to remove impurities and neutralize flavours. Although it may have a higher smoke point for cooking, it loses some of the natural antioxidants and health benefits found in unrefined olive oils (1).
Types Of Butter
Butter, a classic ingredient loved for its creamy taste and rich texture, is derived from animal milk. It is made by churning milk or cream to separate the butterfat from the buttermilk. Butter comes in various forms, but let us focus on the two most common types:
- Salted butter: This type of butter contains added salt, which enhances its flavour but also increases sodium intake. While salted butter can be delicious in moderation, excess sodium intake may pose health risks, particularly for individuals with high blood pressure. If you are watching your sodium intake be sure to check out this post on low sodium cookbooks, and this section on low sodium recipes.
- Unsalted butter: As the name suggests, unsalted butter is made without added salt. It is a versatile option for cooking and baking, offers a more neutral flavour profile, and allows for better control of sodium consumption.
However, it still contains high levels of saturated fats, which can contribute to high cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease, cardiovascular disease or stroke (3).
You can identify saturated fat in a product because it remains solid at room temperature. A key difference between olive oil vs butter. Saturated fat is typically higher in animal products like animal fats like butter vs. oils.
Nutritional Breakdown Of Olive Oil vs. Butter
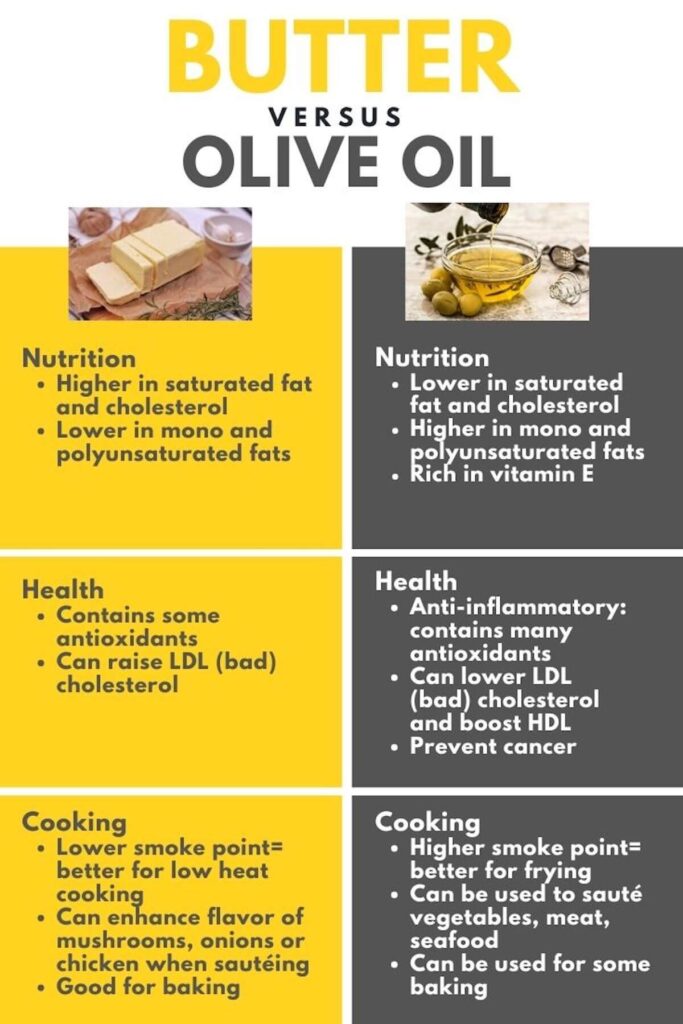
Are you ready to see the nutritional showdown between olive oil and butter? Brace yourself for some eye-opening differences, particularly with regards to saturated fat and antioxidants:
| Nutrient | Olive Oil (1 tbsp) | Unsalted Butter (1 tbsp) |
| Calories | 119 kcal | 102 kcal |
| Total Fat | 13.5g | 11.5g |
| Saturated Fat | 1.86g | 7.17g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 9.86g | 3.32g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 1.42g | 0.43g |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 31 mg |
| Vitamin E | 1.94mg (10% DV) | 0.33mg (2% DV) |
Table 1: Nutritional breakdown of olive oil vs unsalted butter per 1 tbsp (All data are derived from USDA Food Data Central) Note: Nutritional values may vary slightly depending on the brand and specific type of olive oil and butter used.
As you can see, there are some notable differences. Extra-virgin olive oil triumphs over butter with significantly lower levels of saturated fat and cholesterol. But that’s not all! Olive oil boasts higher amounts of heart healthy fats like monounsaturated fatty acids and polyunsaturated fats, which is why the Mediterranean diet and olive oil are recommended for heart health (4).
Besides, olive oil is rich in Vitamin E, which is a great antioxidant that shields our cells from damage caused by free radicals. Which is why olive oil can lower blood pressure.
When it comes to our heart’s well-being, vitamin E has some impressive perks. It helps keep our arteries in check by preventing the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol aka the “bad” cholesterol, a process linked to the development of artery-clogging plaques. Research shows that a higher intake of antioxidants is linked to a lower risk of coronary heart disease (4).
So, when it comes to choosing a nutritional champion, olive oil is the best choice and takes the crown with its impressive composition. It’s time to embrace the healthier alternative and savor the benefits to overall health it offers!
Health Benefits
But wait, there’s more to this battle! Let’s explore the potential health benefits of olive oil and butter.
Anti-Inflammatory
Get ready to fight inflammation with olive oil as your secret weapon!
Olive oil contains powerful antioxidants and compounds, such as oleocanthal, which possess anti-inflammatory properties (5). These antioxidants can help calm down the body’s inflammatory response and provide relief. So, next time you savor a drizzle of olive oil on your salad (like with this cherry vinaigrette!), know that you are giving your body a natural defense against inflammation.
While butter may not offer the same inflammation-fighting benefits, it does contain small amounts of antioxidants like beta-carotene, and vitamin E.
Heart Healthy
Your heart deserves some love, and olive oil is here to deliver!
Olive oil has been extensively studied and shown to be a heart-healthy choice. The monounsaturated fats it contains can help lower LDL cholesterol levels, boost high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol aka the “good” cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and keep your heart in top shape (2).
On the flip side, butter’s high saturated fat content has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease as they can raise LDL cholesterol levels (3). So, choose wisely for a happier heart!
Prevent Cancer
While olive oil cannot single-handedly defeat cancer, it does possess some impressive properties that may help reduce the risk.
Extra virgin olive oil is rich in polyphenols and other bioactive compounds that have been linked to potential anticancer effects. Research suggests that regular consumption of olive oil, as part of a balanced diet, may help lower the risk of certain cancers, such as breast and colorectal cancer (6).
Hence, let olive oil be your ally in the battle against cancer!
Which Is Better For Cholesterol And Heart Health?
When it comes to cholesterol and heart health, olive oil takes the spotlight as the healthier option as it is part of the DASH diet, Mediterranean diet, and MIND diet .
Unlike butter, which is high in saturated fat, olive oil is primarily composed of heart-healthy monounsaturated fats. These fats have been shown to have positive effects on cholesterol levels by reducing the “bad” LDL cholesterol and increasing the “good” HDL cholesterol.
Numerous studies have consistently demonstrated that replacing saturated fats, such as those found in butter, with monounsaturated fats, like those found in olive oil, can lead to improvements in cholesterol profiles and reduce the risk of heart disease, including coronary heart disease and high blood pressure(1).
Therefore, when it comes to making a choice that promotes better cholesterol and heart health, incorporating olive oil into your diet is a wise decision.
Cooking Properties
Olive oil and butter each have their own unique characteristics and are better suited for different cooking methods, dishes, and cuisines. By understanding their strengths, you can select the right ingredient to elevate your cooking and create delicious dishes!
- Frying: Olive oil has a higher smoke point, making it a better choice for high heat frying methods like deep frying or stir-frying. Butter, on the other hand, has a slightly lower smoke point and is more prone to burning, making it suitable for lower heat cooking techniques. Try this tofu Bolognese for a heart health meal using olive oil.
- Sautéing: Olive oil is versatile and can be used for sautéing a wide range of ingredients, including vegetables, meats, and seafood. It adds a light, fruity flavor to the dish. Butter, with its rich and creamy taste, can enhance the flavor of foods like mushrooms, onions, or chicken in a sautéed dish. Try this low sodium marinara sauce that uses olive oil.
- Baking: Butter is often the preferred choice for baking due to its distinct flavour and ability to add moisture and richness to baked goods. It helps create a tender texture and adds a delicious taste to cakes, cookies, and pastries. However, olive oil can also be used in certain baking recipes, particularly those that call for oil-based batters or recipes that aim for a more moist and dense texture. Or try this baked salmon recipe using olive oil.
Smoke Point
You may have heard of the term “smoke point” of oil or fat, but are unsure what they exactly are?
The smoke point of an oil or fat essentially refers to the temperature at which it begins to smoke and break down, leading to the release of unpleasant flavours and potentially harmful compounds. Here are the approximate smoke points for olive oil and butter:
- Olive oil: The smoke point of olive oil can vary depending on the type of olive oil. Extra virgin olive oil, which is unrefined and retains more of the natural compounds and flavours, has a lower smoke point of around 320°F (160°C). Refined olive oil, which undergoes additional processing, has a higher smoke point of about 390-470°F (199-242°C) (7).
- Butter: The smoke point of butter is relatively low due to its milk solids and moisture content. Regular unsalted butter has a smoke point of approximately 302°F (150°C) (7).
When cooking at high temperatures, it is advisable to choose oils or fats with higher smoke points to avoid the development of unpleasant flavours and potential health risks associated with overheating.
Please always be mindful of the cooking method, temperature, and the specific requirements of your recipe to ensure the best results and maintain the integrity of your chosen oil or fat. Check out this awesome article about olive oil substitutes if you are cooking at higher heat.
Taste And Flavor
When it comes to taste and flavour, olive oil and butter offer distinct profiles that can enhance different types of foods and dishes.
- Olive Oil: Olive oil brings a unique taste and flavour to the table. Extra virgin olive oil, known for its robust flavour, offers a fruity, grassy, and sometimes peppery taste. It adds a pleasant, distinct character to salads, dressings, and Mediterranean-inspired dishes like pasta, roasted vegetables, and grilled meats.
- Butter: Butter, with its rich and creamy nature, offers a delightful combination of richness, slight sweetness, and a subtle hint of saltiness. Butter can elevate a multitude of dishes, from classic baked goods like cookies, cakes, and pastries to savory preparations like sauces, sautéed vegetables, and pan-fried meats.
Whether you choose between olive oil and butter depends on your desired flavour and culinary style.
- Olive oil’s fruity and grassy notes work well with fresh salads, drizzled over grilled vegetables, tossed with pasta, or used as a finishing touch on soups or bruschetta.
- Butter’s creamy richness lends itself well to baked goods, where it contributes to tender textures and delightful flavours. It also adds depth to creamy sauces and enhances the flavours of sautéed vegetables.
Culinary Uses
Now that you understand olive oil and butter, you may ask yourself how to use them in the kitchen. Olive oil and butter are versatile ingredients that can be used in a wide range of dishes and recipes, each imparting its own unique flavor and texture.
Olive Oil:
- Salad dressings: Olive oil forms the base of many salad dressings, providing a fruity and slightly peppery flavour that complements fresh greens and vegetables.
- Pasta dishes: Olive oil can be drizzled over cooked pasta to add richness and prevent sticking, while its distinctive flavour enhances the overall taste of the dish.
- Roasted vegetables: Tossing vegetables in olive oil before roasting helps to enhance their natural flavours, add a touch of richness, and create a crispy texture.
- Grilled meats and seafood: Brushing olive oil onto meats or seafood before grilling helps to seal in moisture and prevent sticking.
Butter:
- Baked goods: Butter is a staple in baking, contributing to the rich and tender texture of cookies, cakes, pastries, and pie crusts. Its creamy flavour enhances the overall taste of these treats.
- Sauteed and pan-fried dishes: Butter’s high-fat content and rich flavour make it perfect for sautéing vegetables, searing meats, or pan-frying delicate seafood.
- Creamy sauces and gravies: Butter is often used as a base for creamy sauces and gravies, contributing to their velvety texture.
Sustainability
If you consider yourself to be an environmentally conscious consumer, you might be wondering which of these two products are more eco-friendly. Let’s delve into these aspects for a better understanding:
Land Use:
- Olive oil: the land use associated with olive oil production tends to be more sustainable. Olive trees can grow in marginal lands, often with low water and nutrient requirements, making them suitable for cultivation in arid or semi-arid regions.
- Butter:In contrast, butter production relies on dairy farming, which requires more land for grazing and growing animal feed.
Water Consumption:
- Olive oil: Olive trees are more drought-tolerant than the crops grown for animal feed, making olive oil production generally less water-intensive.
- Butter: Butter production, on the other hand, requires significant amounts of water for cattle farming and the production of animal feed.Dairy farming, including butter production, can have a significant water footprint due to the water required for cow hydration, feed crops, and cleaning processes.
Carbon Emissions:
- Olive oil: Olive oil production typically has a lower carbon footprint compared to butter production. Olive trees can also act as carbon sinks, sequestering CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Butter: Butter production, on the other hand, involves cattle farming, which contributes to methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas.
Another point to note is some ethical and social issues regarding the production of butter and olive oil.
When considering animal welfare in butter production, there are concerns related to the treatment of dairy cows, including their living conditions, access to pasture, and proper healthcare.
Sustainable and ethical butter production involves ensuring the well-being of cows, such as providing them with ample grazing opportunities and comfortable housing.
In contrast, olive oil production does not directly involve animal welfare. Sustainable olive oil production can contribute to overall environmental sustainability by implementing practices such as organic farming, conservation of biodiversity, and responsible water and land management.
Cost
How much do olive oil and butter cost? And which one is more affordable and cost-effective? You might wonder.
The answer is: depending on the brands, your location, and cooking needs.
For example, Walmart.ca sells a 750 mL Kriti Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil for $10.47 plus tax, or approximately $1.40/100 mL. On the other hand, it will cost you $7.98 or $1.76/100 g for a Gay Lea Unsalted Butter Stick when you shop at the same place.
The choice between olive oil and butteralso depends on your specific cooking needs and preferences. Below are some considerations:
- Olive oil can be a cost-effective option when used sparingly due to its strong flavour profile. All you need is to add just a small amount and it can go a long way in providing taste and richness to dishes like salads, pasta, and grilled vegetables.
- Butter, while being generally more expensive than olive oil, is often loved for its rich taste and unique ability to enhance the flavour and texture of baked goods, sautéed dishes, and creamy sauces.

How They Are Used In The Mediterranean Diet
If you have followed my blogs for quite a while, you may have read my article on the Mediterranean diet, what it is, and the health benefits it offers.
In general, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes a plant-based eating pattern, with a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, fish, and lean proteins, complemented by the moderate use of olive oil as the primary fat source.
It is consumed in larger quantities compared to butter, which is used more sparingly and for specific culinary purposes. Here is how olive oil and butter are typically used in the Mediterranean diet:
Olive Oil:
- Cooking: Olive oil is widely used for cooking, including sautéing, frying, and baking. It is used in various Mediterranean dishes, such as grilled vegetables, seafood, and poultry.
- Dressings and marinades: Olive oil serves as a key ingredient in salad dressings, vinaigrettes, and marinades, adding flavour and richness to salads, vegetables, and meats.
- Dips and Spreads: Olive oil is used in popular Mediterranean dips and spreads like hummus, baba ganoush, and tapenade, providing a smooth texture and distinct taste
Butter:
- Butter is less commonly used in traditional Mediterranean cuisine compared to olive oil. It is typically used in Mediterranean baking, such as for making pastries, cookies, cakes, and shortbread.
How To Replace Butter With Olive Oil
Replacing butter with olive oil in various culinary applications is a heart-healthy alternative that can add a unique flavour profile to your dishes. Below are some simple yet creative ways you can substitute butter with olive oil:
- Spreading on toast: Instead of spreading butter on toast, try drizzling olive oil over it. Choose a high-quality extra virgin olive oil for a rich flavor. You can also add herbs or spices to enhance the taste.
- Cooking: When sautéing vegetables or protein, you can use olive oil instead of butter. Heat the oil in a pan and add your ingredients. The oil will provide a nice coating and add flavor to the dish.
- Salad dressings: You might replace the butter in homemade salad dressings with olive oil. Simply combine olive oil with vinegar or lemon juice, herbs, spices, and a touch of honey or mustard for a tasty dressing.
- Dips and Spreads: You can totally create flavorful dips and spreads by using olive oil as a base! Combine it with ingredients like roasted garlic, herbs, spices, hummus, and yogurt or tahini for a creamy and healthy dip.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Better For You Butter Or Olive Oil?
Olive oil is better for you compared to butter due to its higher content of heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and lower levels of saturated fat, which can help improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Which Is Healthier Butter Or Oil?
Olive oil is healthier than butter because it contains healthier fat profile as well as many beneficial antioxidants. Butter, on the other hand, contains high levels of saturated fats, which can contribute to elevated LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
Is Olive Oil A Healthy Substitute For Butter?
Yes, olive oil is a healthy substitute for butter!
In many baking recipes that call for butter, you can substitute it with olive oil. Use a 3/4 ratio, meaning if a recipe calls for 1 cup of butter, use 3/4 cup of olive oil instead. This substitution works well in cakes, muffins, and bread.
Is Butter Or Olive Oil Less Fattening?
Olive oil is less fattening than butter since it contains fewer calories per gram.
However, moderation is still key as both olive oil and butter are calorie-dense and should be consumed in appropriate amounts to maintain a healthy weight.
Recipes That Use Olive Oil For Heart Health
Here are some heart-healthy recipes that call for olive oil you may be interested in:
Final Thoughts
As you have now read, olive oil reigns supreme when it comes to promoting heart health. Its abundant reserves of heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, antioxidants, coupled with its lower levels of saturated fat, make it a better choice than butter.
By incorporating olive oil in your daily cooking, you will unlock a world of flavors, nourishment, and protection for your precious hearts. Let olive oil be your trusted companion on the journey to a healthier heart and a more vibrant life!
Don’t forget to try out the recipes and let me know how you like them in the comment section below. Enjoy!
This article was written by Wesley Mai Nutrition Student, and Veronica Rouse, MAN, RD, CDE.




