Maybe you or someone you know is currently living with high blood pressure and are wondering if oats are good for blood pressure.
High blood pressure is a concern for many people, as nearly 1 in 5 people in North Americans are living with it (1).
You may have heard of different foods that are good for lowering blood pressure, and oats are probably one of them.
There are many health benefits of oatmeal that can lower blood pressure, so if you are someone looking for ways to lower blood pressure with oats and understand how fast oatmeal can lower blood pressure, this article will be helpful for you!
Top Takeaways
- Oats are considered beneficial for managing high blood pressure due to their rich content of soluble fiber, particularly beta-glucan, which helps prevent atherosclerosis and lowers blood pressure.
- Oats also contain minerals like potassium, calcium, and magnesium, which relax blood vessels and contribute to blood pressure control.
- The antioxidants in oats, called avenanthramides, reduce inflammation and combat the effects of free radicals, further promoting lower blood pressure.
- Incorporating oatmeal into your daily diet, along with a focus on whole, unprocessed foods, regular exercise, and limited salt, saturated fat, and sugar intake, can be effective in controlling high blood pressure.
- Top Takeaways
- Pin It For Later!
- What Is High Blood Pressure & Why Is It A Concern
- Does Oatmeal Lower Blood Pressure – The Link!
- Nutritional Benefits Of How Oatmeal Can Lower Blood Pressure
- Oats And High Blood Pressure Diet
- Other Health Benefits Of Oatmeal
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Other Ways To Control Blood Pressure
- Other Foods That Can Lower Blood pressure
- Final Thoughts
Pin It For Later!
What Is High Blood Pressure & Why Is It A Concern
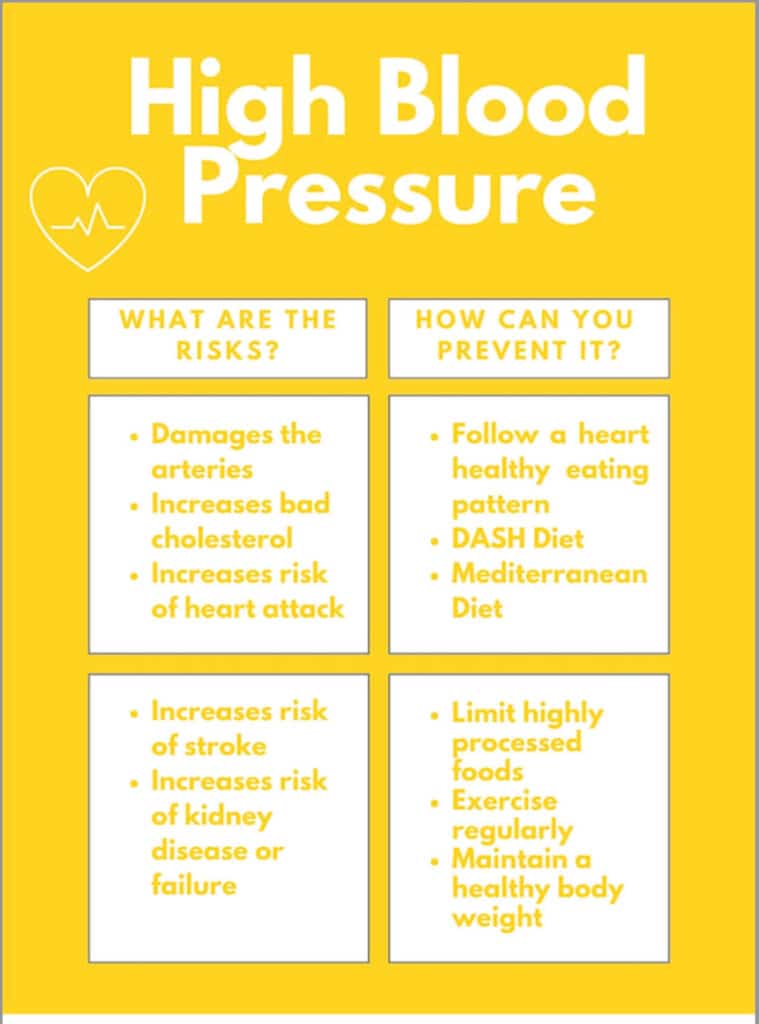
High blood pressure is when the force put on the artery walls by the blood is consistently too high.
There are many serious health concerns associated with high blood pressure including heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease (2).
Having high blood pressure can damage arteries and cause an accumulation of bad cholesterol. This condition is called atherosclerosis. It narrows the arteries which puts strain on your heart since it must work harder to pump your blood. This increases the risk of heart attack, stent placements, peripheral artery disease, or heart failure.
There is also a greater risk for stroke if the brain is not supplied with enough blood flow and oxygen (which is carried in the blood). If the arteries that supply blood to the brain become damaged, this reduced blood flow may occur and lead to a stroke.
Finally, high blood pressure can lead to kidney disease. The kidneys are responsible for filtering our blood to remove any harmful substances through our urine. If there is damage to the arteries involved in the filtration process, the kidneys will not be able to function properly.
These are just a few of the main concerns with high blood pressure, but there are many other issues that can potentially arise.
Now that we know that high blood pressure is something we want to manage. Let’s see if oats can lower blood pressure.
Does Oatmeal Lower Blood Pressure – The Link!
It is recommended that those with high blood pressure follow a “heart healthy” eating pattern, like the DASH diet. One of the components of the DASH diet is to include whole grains and unprocessed foods.
Oats are a great option for an unprocessed, whole grain that you can include in your diet.
Oats are good for lowering blood pressure mainly because they contain a type of soluble fiber called beta-glucan that will be discussed in the next section.
Nutritional Benefits Of How Oatmeal Can Lower Blood Pressure
Fiber Content
Oats are rich in both soluble and insoluble fiber which both help with digestion. Insoluble fiber helps to build bulk and soluble fiber forms a gel-like substance and helps to slow the digestion process.
Oats are rich in the soluble fiber, beta-glucan, which has been shown to have health benefits including aiding digestion and helping to lower blood sugar and blood cholesterol (3). An essential component of the Portfolio diet. Be sure to check out these oatmeal recipes to lower cholesterol.
There is research that suggests beta-glucan can also play a significant role in lowering blood pressure (4). Thus, oatmeal and lower blood pressure.
Soluble Fiber And Cholesterol Lowering
As mentioned above, soluble fiber can help to lower cholesterol. It does this by binding cholesterol during the digestion process so that it can be excreted in the stool rather than reabsorbed into the bloodstream (5).
Lowering cholesterol can help to lower blood pressure, prevent atherosclerosis, and stroke. Here is a great list of oat bran recipes that can help lower cholesterol.
Check out this list of low cholesterol foods, a 7-day meal plan to lower cholesterol, and 21 natural drinks to lower cholesterol.
Minerals
So why else does oatmeal lower blood pressure? Oats contain some key minerals that may also play a role in lowering blood pressure.
Oats are a good source of potassium, calcium, and magnesium, all of which play a role in relaxing muscles. This includes the blood vessels, and their relaxation helps to control blood pressure (6).
Can Reduce Inflammation
Oats contain antioxidants called avenanthramides which may help to reduce inflammation caused by harmful free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that cause damage to the body andcan contribute to high blood pressure.
Antioxidants are needed to prevent the damage that the free radicals can cause (7). Check out this comprehensive list of anti-inflammatory foods for heart disease to add more foods to your diet.

Oats And High Blood Pressure Diet
DASH stands for “Dietary Approaches to Stopping Hypertension”. The DASH diet is an eating pattern recommended for lowering blood pressure and helping to reduce the risk of heart disease. Oats are part of this blood pressure lowering diet!
One of its suggestions is to eat 7-8 servings of whole grains per day.
Oats are unprocessed whole grains that are high in fiber. Including oatmeal in your diet is a great way to get in a healthy serving of whole grains. Thus, oatmeal can lower blood pressure.
Try this Vegan Protein Oatmeal as a great way to start your day to lower your blood pressure.
Other Health Benefits Of Oatmeal
The other health benefits discussed are all related to the high fiber content of oats.
Better Digestion
Fiber is very important for healthy digestion, especially when it comes to preventing constipation.
As mentioned earlier, oats contain both soluble and insoluble fiber which have different roles in digestion.
Soluble fiber will form a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, helping to retain water. It also helps to slow down digestion and nutrient absorption (8).
Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, is what helps to build bulk and make your stool easier to pass.
Blood Sugar
Fiber plays an important role in controlling blood sugar levels. Having high blood sugar can pose similar health risks as high blood pressure.
In our bodies, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which will be absorbed into the blood from the digestive tract. Glucose is the sugar that is referred to when we talk about blood sugar levels.
After we eat a meal with carbohydrates, our blood sugar levels will rise due to the increase in glucose.
Fiber will not cause this rise in blood sugar because it is a carbohydrate that does not get broken down into glucose. Because of this, it helps to alleviate spikes in blood sugar after a meal (9).
Weight Management
Since fiber slows down digestion and prevents spikes in blood sugar, it helps you to feel full for longer after eating. This can help to prevent overeating which will help to maintain a healthy body weight when done alongside other healthy lifestyle choices.
Cancer
Studies have suggested that consuming a diet rich in fiber may help to lower the risk of breast cancer and colon cancer. Since fiber is often consumed with a variety of other healthy foods, this may be a factor contributing to its ability to lower the risk (10).
Frequently Asked Questions
How Fast Does Oatmeal Lower Blood Pressure?
Oatmeal lowers blood pressure in 6 weeks according to this research study (11).
How Much Oatmeal Should I Eat A Day To Lower Blood Pressure?
3/4 of a cup of dry oatmeal will lower blood pressure according to the study above (11). It’s important to try to incorporate oatmeal throughout the day to reach this amount.
You can try to have it for breakfast, lunch, dinner, dessert, or a snack!
What Does Oatmeal Do To Your Blood?
Oatmeal can help to lower blood pressure, blood sugar, and blood cholesterol. Try these Pumpkin Protein Balls as an easy way to start incorporating oats today!
What Should I Eat For Breakfast To Lower My Blood Pressure?
You should eat oats for breakfast to lower your blood pressure, they are a great option!
There are many ways to prepare oats, whether you prefer oatmeal, baked oats, oat water, or overnight oats.
Other Ways To Control Blood Pressure
Since we answered the question: is oats good for blood pressure? What are some other ways to control blood pressure?
One of the best ways to control blood pressure is to make sure that you are eating a diet full of whole, unprocessed foods. This means limiting high amounts of salt, saturated fat, and sugar.
Some of the recommended dietary patterns to follow are the DASH diet and Mediterranean diet.
Along with eating a well-balanced diet, it is important to exercise regularly, which will help to control blood pressure and maintain a healthy weight.
Other Foods That Can Lower Blood pressure
Apple cider vinegar and baking soda and blood pressure
Pea protein and blood pressure
Final Thoughts
Overall, oats are a nutritious food that offer many health benefits!
If you are looking for a delicious food that will help to lower blood pressure, consider making oats a new staple in your diet.
Do you think oatmeal is good for high blood pressure? Have you tried using oatmeal to lower blood pressure? How fast did oatmeal lower your blood pressure? Tell me in the comments below! Would love to learn from you too.
This article was written by Siobhan Tyler, Nutrition Student, and Veronica Rouse, MAN, RD, CDE.

